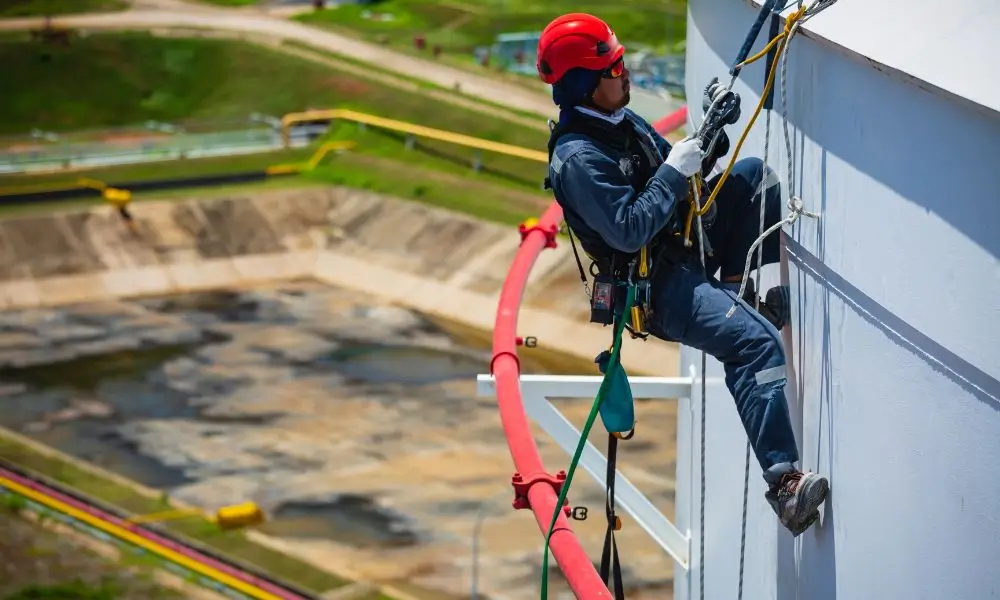
Working at height hazards is a major safety concern in professions such as construction, maintenance, and utilities. When jobs are performed at a significant elevation from the ground, the risk of severe accidents and injuries increases significantly. It is crucial to recognize and address these hazards to ensure a safe working environment.
In this article, we will explore some typical hazards of working at elevated levels and offer practical solutions to minimize these risks. The solutions range from preventing falls from heights to addressing challenges such as unstable platforms and unpredictable weather.
Working At Height Hazards And Control Measures
When working at height, it is crucial to identify hazards and implement control measures to reduce risks. Here are ten common hazards related to working at height, along with suggested control measures:
Failure Of Lifting Equipment

Lifting equipment is vital in many industries, but when it fails, the consequences can be severe. In 2018, a construction site witnessed a tragic accident when a crane’s cable snapped, leading to critical injuries. This incident highlights the need for stringent safety measures.
Control Measures:
- Regular Inspections and Maintenance: Conduct thorough inspections and perform regular maintenance to prolong equipment life. This practice not only ensures safety but also enhances operational efficiency.
- Safe Operation Practices: Always adhere to the manufacturer’s instructions. These guidelines are designed to optimize equipment use while ensuring safety.
- Adhering to Load Limits: It is crucial never to exceed the maximum load limit. Overloading is a common cause of equipment failure and can lead to dangerous accidents.
- Comprehensive Training: Operators should receive in-depth training on both the use and maintenance of equipment. This training should be updated regularly to reflect any changes in equipment or safety standards.
Key Point: Instead of waiting for an incident to occur, take proactive steps to ensure equipment safety. Regular risk assessments, staying updated with the latest safety protocols, and fostering a culture of safety can significantly reduce the likelihood of equipment failure.
Improper Use Of Equipment
The misuse of equipment is a leading cause of workplace accidents. In 2019, improper handling of a forklift in a warehouse led to significant property damage and injuries, underscoring the need for strict adherence to safety protocols.
Control Measures:
- Proper Training and Regular Supervision: Provide comprehensive training on the correct usage of each equipment type. Regular supervision helps reinforce these practices and correct any deviations promptly.
- Enforcement of Safe Practices: Develop and communicate clear safety guidelines. Ensure consistency in their enforcement to cultivate a safety-first mindset among all employees.
- Regular Equipment Checks: Conduct frequent inspections to identify and rectify any usage issues or mechanical faults. This proactive approach helps in maintaining equipment in optimal condition and safe for use.
- Choosing the Right Equipment: Always provide equipment that is suitable for the specific job. Using the wrong equipment can lead to misuse and accidents. Regularly assess the needs of each task and match it with the appropriate tools and machinery.
Reminder: Proactivity in training, supervision, and equipment maintenance is crucial in minimizing the risks associated with equipment misuse. A well-informed and well-equipped workforce is your best defence against workplace accidents.
Falls From Heights
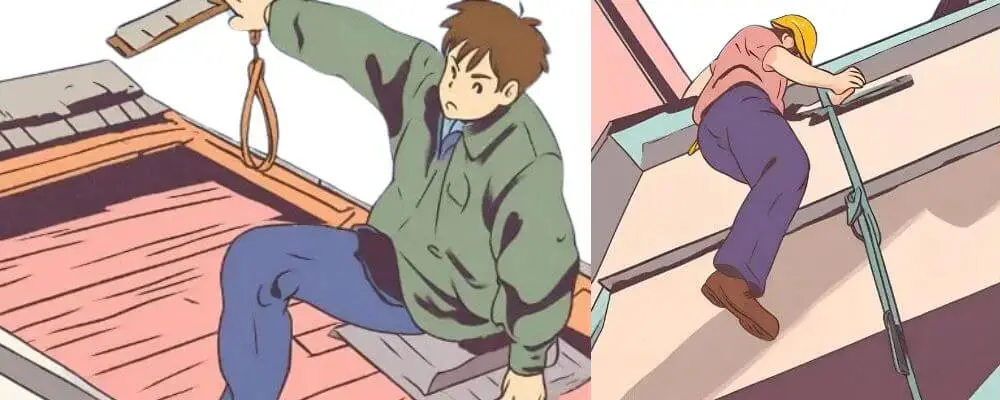

Falls from heights remain a leading cause of workplace fatalities and serious injuries, accounting for a significant percentage of accidents in the construction industry.
Control Measures:
- Guardrails: Implement guardrails as a physical barrier, especially around elevated platforms and walkways, to prevent falls.
- Safety Nets: In areas where installing guardrails is not feasible, such as certain construction sites, use safety nets to catch workers if they fall.
- Personal Fall Protection Equipment: Equip workers with harnesses, lanyards, and retractable lifelines, ensuring they are trained in their proper use.
- Restraint Systems: Utilize restraint systems to prevent workers from reaching edges where falls could occur. This is particularly important in areas where other protective measures are not viable.
- Comprehensive Safety Training: Conduct ongoing education on recognizing fall hazards and correctly using protection equipment. Regular drills and practical demonstrations can enhance this training.
Best Practice Tip: Always seek to eliminate the hazard first. If feasible, conduct work at ground level to significantly reduce the risk of falls. This proactive approach is often the most effective safety measure.
Unstable Working Surfaces
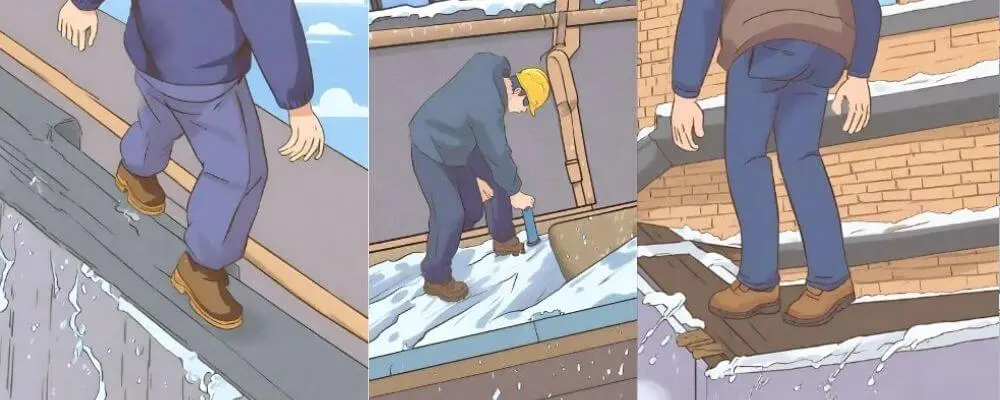

Unstable surfaces, whether uneven or slippery, significantly increase the risk of workplace accidents. These conditions are responsible for a considerable number of slips, trips, and falls annually.
Control Measures:
- Regular Surface Inspections: Conduct frequent inspections to identify potential hazards like uneven flooring or loose tiles. Early identification is key to preventing accidents.
- Application of Slip-Resistant Materials: Use mats, coatings, or other materials that enhance grip and reduce the likelihood of slips and falls, especially in areas prone to wetness or spills.
- Appropriate Footwear: Ensure that all personnel wear shoes or boots with non-slip soles. This simple measure can significantly reduce the risk of slips.
- Diligent Housekeeping: Maintain clean and organized workspaces. Regular cleaning and immediate addressing of spills can greatly enhance surface stability.
- Weather Considerations: In outdoor settings, be prepared to postpone work during adverse weather conditions that exacerbate the risk, such as heavy rain or snow.
Expert Tip: Use the correct equipment for the job. For instance, when using ladders, ensure they are securely footed and appropriate for the surface type. This consideration is crucial in maintaining balance and stability.
Falling Objects
Objects falling from heights are a common hazard, particularly in construction and industrial settings, posing a significant risk to those below. Injuries from such incidents range from minor to fatal.
Control Measures:
- Toe Boards and Netting: Install toe boards at the edges of elevated areas and use safety netting around areas where work is being performed at height. These measures are effective in preventing tools and materials from falling.
- Tool Lanyards: Secure all tools and equipment with lanyards when working at height. This simple yet effective practice prevents tools from accidentally dropping and causing injury.
- Secure Storage: Maintain organized tool storage on scaffolding and elevated work areas. Proper storage ensures that tools and materials are securely placed and less likely to fall.
- Exclusion Zones: Establish exclusion zones under areas where work is performed at height. These zones should be clearly marked and access controlled to prevent personnel from unknowingly walking into high-risk areas.
Insight: Always wear hard hats on sites where there is a risk of falling objects. This basic personal protective equipment is a critical line of defence against head injuries.
Scaffolding Collapse
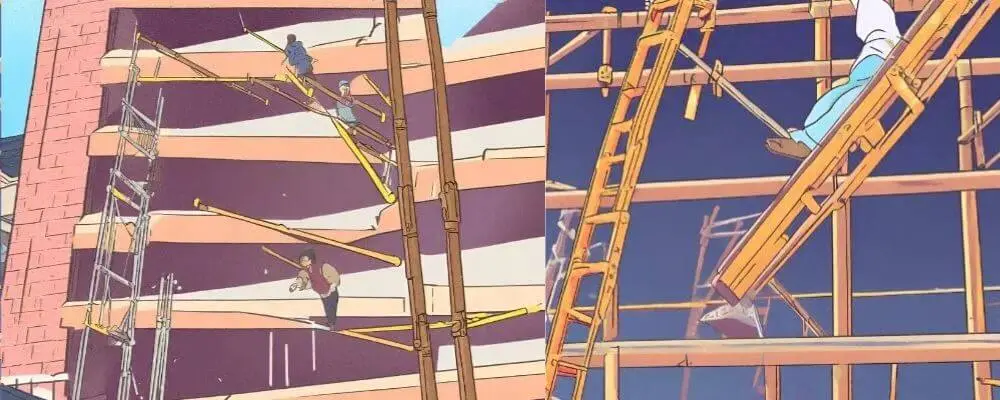

Scaffolding collapses are a serious hazard, often resulting from poor construction or inadequate maintenance. These incidents can lead to severe injuries or fatalities and are a significant concern in construction and maintenance work.
Control Measures:
- Regular Inspections: Ensure that competent personnel conduct frequent and thorough inspections of the scaffolding. These should assess structural integrity, stability, and adherence to safety standards.
- Proper Construction and Adherence to Load Limits: Construct scaffolding following the manufacturer’s instructions and local regulations. It’s vital to understand and never exceed the prescribed load limits to ensure stability.
- Prompt Maintenance and Repair: Address any wear and tear or damage immediately. Regular maintenance and the swift replacement of defective parts are crucial to preventing collapses.
- Vigilance with Weather Conditions: Monitor weather forecasts and respond proactively to adverse weather conditions, such as strong winds or heavy rain, which can compromise scaffolding stability.
Critical Advice: Comprehensive training in safe scaffolding practices for all involved personnel is crucial. This training should cover construction, inspection, maintenance, and emergency procedures.
Lack Of Training
A lack of proper training significantly elevates the risk of workplace accidents. Statistics show that untrained or inadequately trained workers are substantially more likely to be involved in workplace incidents.
Control Measures:
- Comprehensive and Specific Training: Provide training that is tailored to the specific tasks and responsibilities of each worker. This approach ensures that workers are fully equipped with the knowledge and skills relevant to their roles.
- Regular Refresher Courses: Implement ongoing refresher courses to keep workers’ knowledge and skills up to date. This is particularly important in fast-evolving industries or where new technologies are introduced.
- Competency Checks: Conduct regular checks to assess workers’ understanding and application of their training. These checks can identify areas where additional training may be needed.
- Detailed Safety Briefings: For complex or high-risk tasks, conduct specific safety briefings. These briefings should cover potential hazards and the procedures to mitigate them.
Culture Tip: Foster a safety-first mindset among all workers. Encourage open communication about safety concerns and recognize those who consistently adhere to safety protocols. This cultural shift can significantly enhance overall workplace safety.
Inadequate Edge Protection
Inadequate edge protection is a critical hazard, particularly in high-risk environments like construction sites, where it significantly increases the likelihood of falls. Such falls are a leading cause of serious workplace injuries and fatalities.
Control Measures:
- Guardrails and Toe Boards: Install these as preventive barriers around perimeters, roof edges, and open sides. They serve to protect not only against falls but also prevent objects from being accidentally kicked over the edge.
- Safety Netting: Implement safety netting as a secondary layer of protection, particularly in areas where guardrails are impractical or insufficient. They provide a safety catch for both personnel and equipment.
- Fall Arrest Systems: Equip workers with comprehensive fall arrest systems, including full-body harnesses and connecting devices, to safely arrest a fall in progress. Regular training on their use is essential.
- Safety Monitoring Systems: Designate a competent and trained individual to supervise and monitor work near edges. This person is responsible for ensuring that safety measures are actively observed and maintained.
Important Reminder: For optimal edge safety, it’s crucial to integrate multiple protective measures. This layered approach significantly enhances overall safety, drastically reducing the risk of falls and related accidents.
Lack Of Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Inadequate personal protective equipment (PPE) significantly increases the risk of workplace injuries. Studies have shown that proper PPE use can reduce the severity and frequency of these injuries.
Control Measures:
- Providing Appropriate PPE: Equip workers with PPE that is specifically tailored to the work conditions and hazards. This may include helmets, gloves, safety glasses, or hearing protection, depending on the task at hand.
- Training in PPE Use: Conduct thorough training sessions for workers on the correct application, use, and maintenance of their PPE. This training should also cover the importance of PPE in preventing injuries.
- Enforcement of PPE Use: Regularly monitor PPE use and implement disciplinary measures for non-compliance. Consistent enforcement helps to establish the importance of PPE in maintaining workplace safety.
Adaptation to Changing Conditions: Be prepared to adjust PPE requirements based on changing work conditions or new hazards. Regular risk assessments can help identify these needs.
Poor Weather Conditions
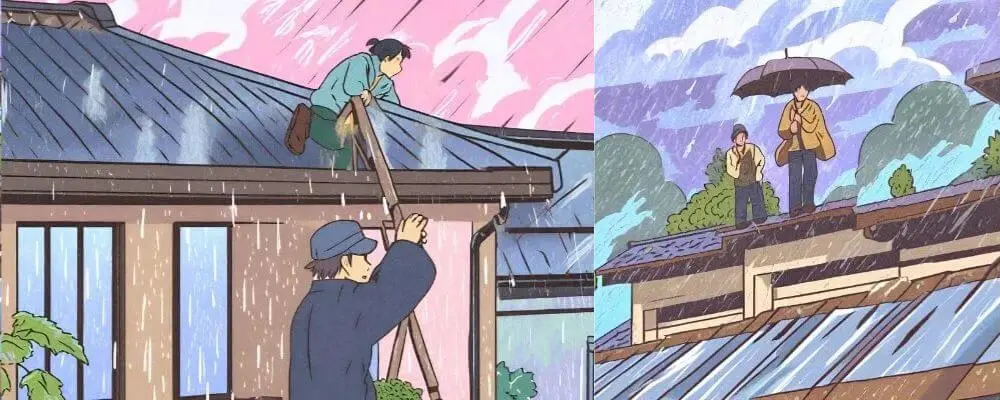

Adverse weather, including extreme temperatures, rain, snow, and wind, can significantly increase workplace risks, especially in outdoor environments. These conditions can lead to hazards such as slippery surfaces, reduced visibility, and exposure-related health problems.
Control Measures:
- Postponing Work: When forecasts predict dangerous conditions, it’s often safest to postpone work. This decision can prevent accidents caused by hazardous weather.
- Weather Monitoring: Stay informed about the latest weather forecasts and advisories. This ongoing vigilance allows for timely decision-making regarding work schedules and necessary precautions.
- Proper Clothing and Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Ensure that workers have access to clothing and PPE suited to various weather conditions, such as waterproof gear for rain, thermal wear for cold, and breathable fabrics for heat.
- Comprehensive Training: Educate workers about the hazards associated with different weather conditions and how to mitigate them. This training should include how to recognize early signs of weather-related health issues like heatstroke or hypothermia.
Important: Regularly inspect work surfaces and environments during varying weather conditions to identify new risks and ensure that safety measures are adapted accordingly.
Additional Working At Height Hazards
| Hazard | Control Measure |
|---|---|
| Poor Conceptual Design | Addressing structural and functional design issues. |
| Signalling Systems Malfunction | Ensuring proper use and maintenance. |
| Loads Insecurely Attached | Implementing strict attachment procedures. |
| Poor Structural Design | Conduct structural integrity assessments by qualified engineers. |
| Unprotected Edges and Openings | Install guardrails and safety barriers. |
Conclusion
Working at height hazards inherently presents a spectrum of risks; however, these can be substantially reduced through the proactive identification of hazards and the diligent implementation of appropriate control measures. Paramount to this endeavour is the provision of comprehensive training, the correct utilization of Personal Protective Equipment (PPE), and unwavering adherence to safety regulations. While this guide serves as a primer on fundamental hazards and their mitigations, it is crucial to conduct regular, detailed risk assessments that are specifically tailored to the unique conditions and challenges of each working environment. The cornerstone of effective workplace safety lies in the synthesis of constant vigilance, robust education, and a deep-seated commitment to cultivating and maintaining a culture of safety. It is imperative to consistently prioritize safety, ensuring that it remains at the forefront of all operational considerations. Stay vigilant, stay educated, and above all, stay safe.
Please Like Our Facebook Page
